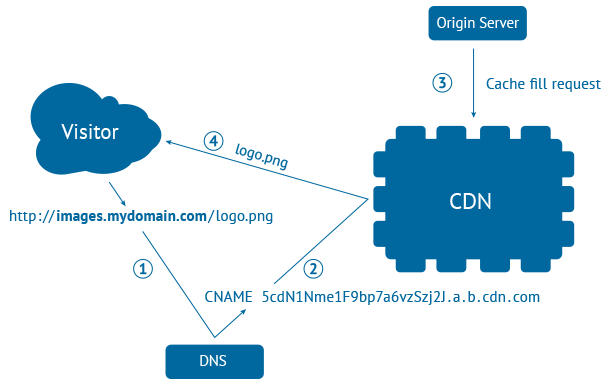
Content delivery network (CDN) is an important technological development to serve the content on the World Wide Web. The core function of a CDN is to increase speed for opening web pages and saving bandwidth. However, modern CDNs provide additional features and make your website less vulnerable to malicious attacks.
When talking about CDNs, many people wonder how does a CDN work. How it increases the speed of web browsing and saves the bandwidth. In the following paragraphs, we will explain the basic concept of a CDN and how it works.

To know more about content delivery networks (CDNs), we must have a basic understanding of how pages are served on the World Wide Web. To visit a website, the user enters a website address in the browser. The address looks similar to http://www.example.com. However, the user’s browser cannot communicate by the means of this kind of text address. To communicate, the browser needs an IP address. When a browser requests the web address, a DNS server translates this text address into an IP address. Now that the user’s browser knows the IP address, it can fetch the required files and serve it as a web page.
To understand the CDN, let us look at a simple example. Suppose a website is located in the United States and people from China, the UK, and the UAE want to access the website. Normally, all the users will be served the files located in the united states. However, if the website uses CDN, and the CDN has servers in China, the UK, and the UAE, every user will receive the files from the nearest server. It is more efficient to use the server in China to serve the files to a user located in China, rather than fetching data from the US server every time the data is requested.